Processes are the foundation of almost every business and play a crucial role in its success or failure. The ability to efficiently manage customers and internal resources through various business processes such as sales, onboarding, billing, customer service and more is essential to building and maintaining profitable relationships.
To achieve true operational excellence, it is essential for a company to first understand the nature of the improvement program it is seeking to implement, define the goals of that program and determine the best way to incorporate technology into those processes.
Many companies are turning to Business Process Improvement (BPI) and Business Process Management (BPM) programs to increase operational efficiency and gain a competitive advantage.
In many companies, these terms are often used interchangeably or have different meanings depending on the context. However, it is important to recognize some key differences between these two concepts.
Both concepts deal with business processes or workflows. A business process can be described as a series of interrelated steps or activities that may span different people, roles or systems. A process is often represented by a flowchart.
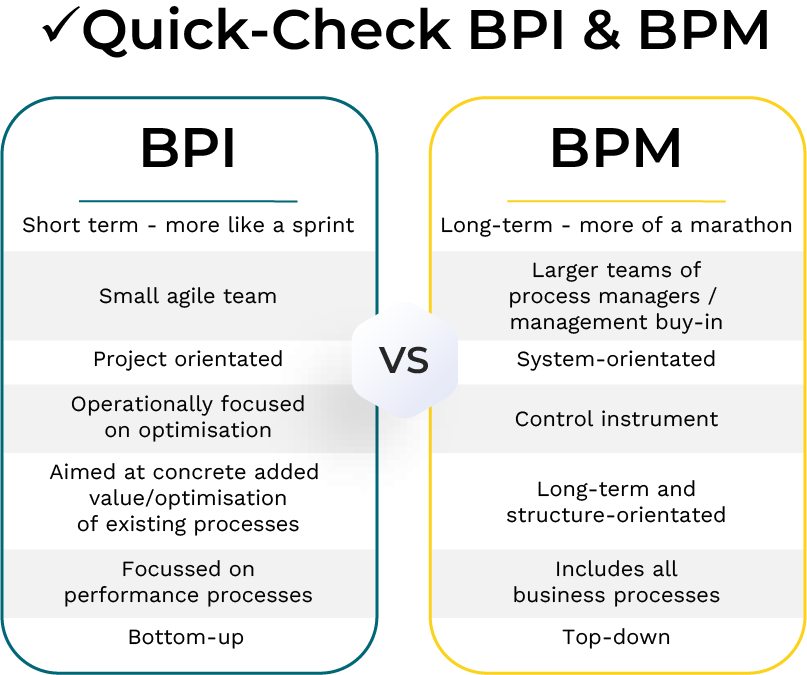
Definition: What is BPM and BPI?
BPM (Business Process Management): BPM is a systematic approach to identifying, documenting, monitoring and continuously improving all business processes in an organization. It includes technologies, methods and techniques to control processes and ensure that they run efficiently and effectively.
BPI (Business Process Improvement): BPI is a project-oriented approach and focuses on rethinking existing individual business processes and making them more effective. The aim is not only to make processes faster and more cost-efficient, but also to improve the quality of the results.
Objective
BPM: The aim of BPM is to create a structured environment in which processes can be clearly defined, monitored and controlled. Business Process Management (BPM) represents a structured management approach and methodology that promotes a comprehensive understanding of processes, their transparency and control, while ensuring effective communication throughout the organization. BPM integrates business process improvement (BPI), performance management and change management (OCM) with technology solutions to ensure the success and sustainability of process optimization and establish a culture of process quality.
BPI: Business process optimization is an approach that aims to increase customer value by continuously improving quality, enhancing customer service, reducing costs and increasing efficiency in activities or business processes. Business Process Improvement (BPI) initiatives often rely on proven methodologies such as Lean, Six Sigma, or Total Quality Management.
These BPI initiatives can either aim for incremental improvement over time by focusing on individual end-to-end business processes, or aim for a radical, one-time improvement that represents an entirely new way of doing business. As a rule, BPI initiatives should precede all digitization and automation efforts, as this prevents inefficient analogue processes from being digitized.
Time horizon
BPM: As BPM takes a holistic and systemic approach, it is often an ongoing process that is re-evaluated at regular intervals. BPM therefore ties up a lot of human resources.
BPI: BPI projects usually have a clearly defined start and end. Once an improvement has been implemented, the process can be transferred to the regular BPM cycle.